



The CYFIRMA Industry Report delivers original cybersecurity insights and telemetry-driven statistics of global industries, covering one sector each week for a quarter. This report focuses on the manufacturing industry, presenting key trends and statistics in an engaging infographic format.
Welcome to the CYFIRMA infographic industry report, where we delve into the external threat landscape of the manufacturing industry over the past three months. This report provides valuable insights and data-driven statistics, delivering a concise analysis of attack campaigns, phishing telemetry, and ransomware incidents targeting the manufacturing industry.
We aim to present an industry-specific overview in a convenient, engaging, and informative format. Leveraging our cutting-edge platform telemetry and the expertise of our analysts, we bring you actionable intelligence to stay ahead in the cybersecurity landscape.
CYFIRMA provides cyber threat intelligence and external threat landscape management platforms, DeCYFIR and DeTCT, which utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to ingest and process relevant data, complemented by manual CTI research.
For the purpose of these reports, we leverage the following data from our platform. These are data processed by AI and ML automation based on both human research input and automated ingestions.
While this report contains statistics and graphs generated primarily by automation, it undergoes thorough review and enhancement for additional context by CYFIRMA CTI analysts to ensure the highest quality and provide valuable insights.
Manufacturing organizations featured in 5 of the 5 observed campaigns, which is a presence in 100% of all campaigns. This is a decrease from 6 observed campaigns in the previous 90-day period.
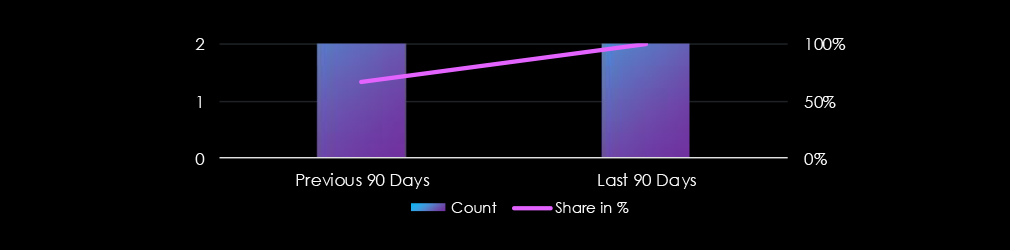

After a calm January, campaigns spiked in February and continued in March.
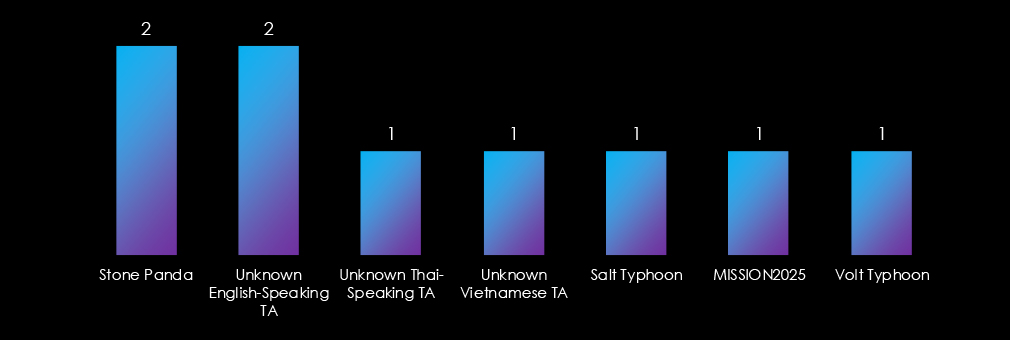
Observed campaigns are conducted by a diverse range of threat actors, most prominently Chinese nation-state groups and also unidentified Vietnamese, Thai, and English-speaking groups, suggesting financial motivations are still prevalent in the Manufacturing industry.
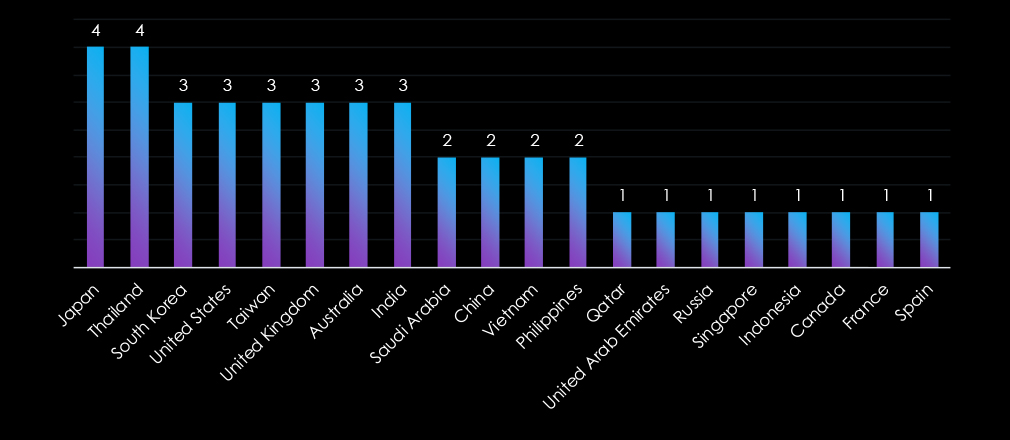
Victims of the observed attack campaigns have been recorded in 20 different countries. Japan and Thailand recorded the most victims. Since there is significant financial motivation for these campaigns, we can see a quite scattered geography, which is in line with the opportunistic nature of financially motivated cybercrime.
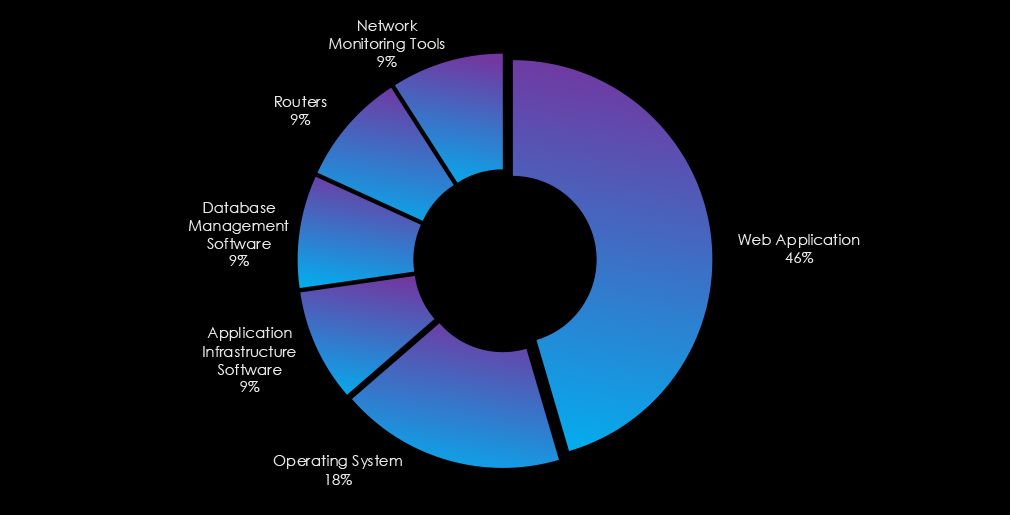
The observed campaigns mostly targeted web applications, followed by operating systems. Furthermore, database management software, routers, network monitoring tools, and application infrastructure software were also targeted.
In the past 90 days, manufacturing organizations have been significantly affected by advanced persistent threat (APT) campaigns. 5 in 5 observed APT campaigns targeted the manufacturing industry, representing 100% presence.
This is one less from the previous 90-day period, where 6 out of 10 campaigns targeted the manufacturing industry. However, the increase in overall presence is more concerning.
Monthly Trends
January did not record any campaigns and then activity spiked during February and continued in March.
Key Threat Actors
About half of the activity is attributed to Chinese threat actors Salt Typhoon and Volt Typhoon. But we have also seen financially motivated Thai, Vietnamese, and English-speaking groups.
Geographical Impact
The campaigns have affected a total of 20 countries, with scattered geography in line with the opportunistic nature of financially motivated cybercrime. The most affected were Japan and Thailand.
Targeted Technologies
Web applications and operating systems remain the most frequently targeted technology. Additionally, database management, routers, network monitoring tools, and application infrastructure software have been compromised.
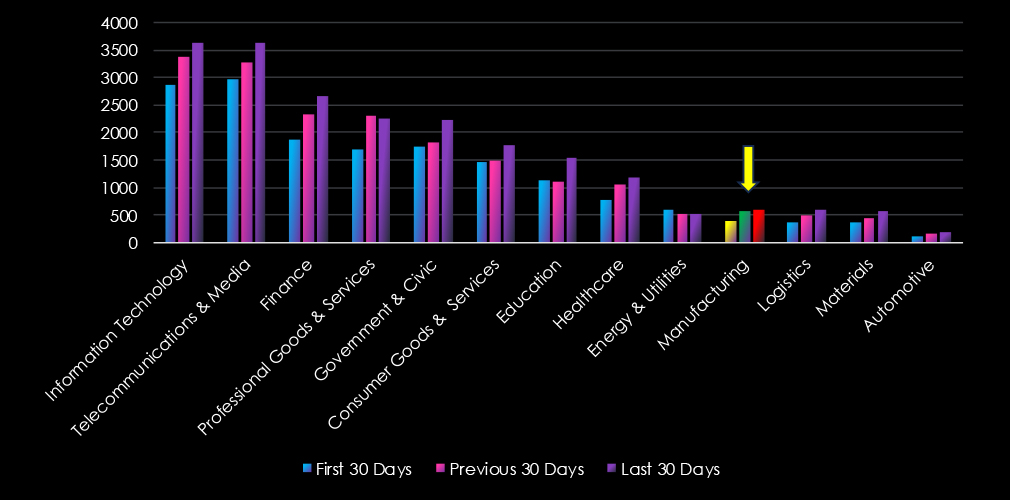
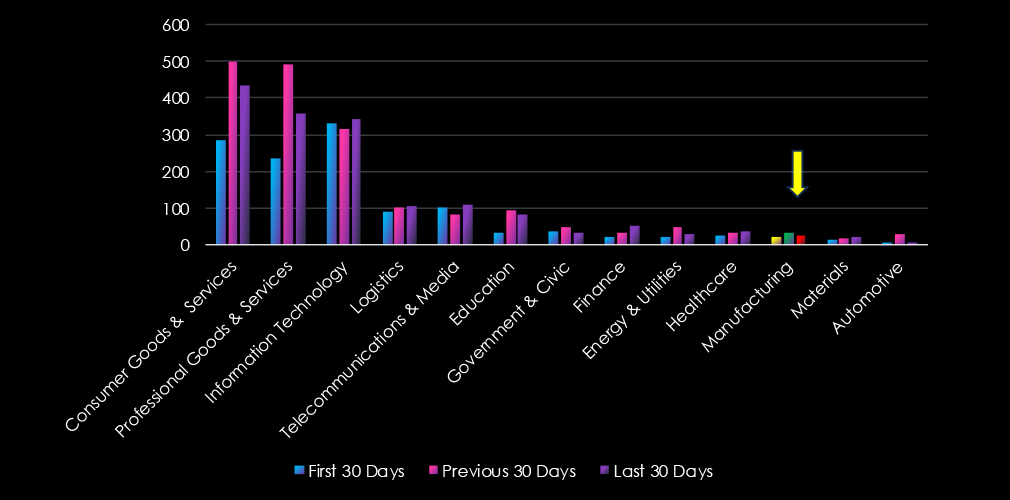
Over the past three months, CYFIRMA’s telemetry has identified 1,562 mentions of manufacturing out of a total of 56,661 industry mentions. This is from a total of 523,813 posts across various underground and dark web channels and forums.
Manufacturing ranked 10th out of 13 industries in the last 90 days with a share of 2.76% of all detected industry chatter.
Below is a breakdown of 30-day periods of all mentions.
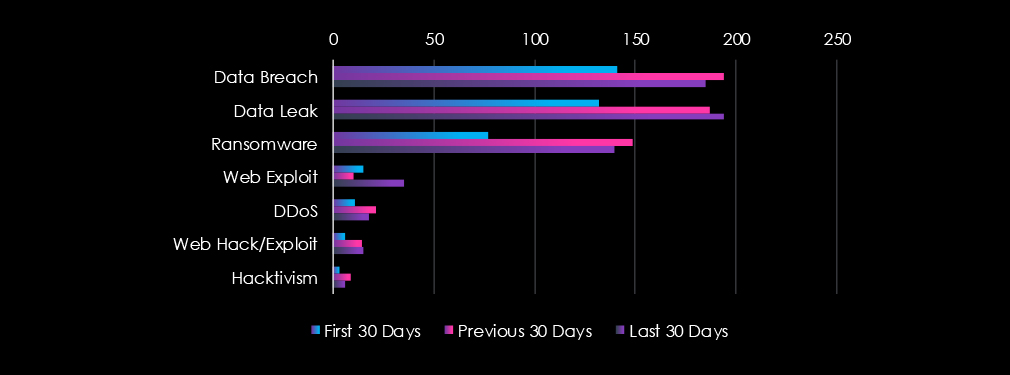
Data breaches, data leaks, and ransomware were the top three categories of recorded cyber threats for the manufacturing industry.
In total, manufacturing comprises 2.76% of all detected industry underground and dark web chatter in the last 90 days and ranks 10th out of 13 industries.
Below are observed key trends across 90 days.
Sharp Increase in Threat Mentions (+54%)
Jan: 385 → Feb: 584 → Mar: 593
A major spike in February, with sustained high activity in March.
Top Threats (March 2025)
Ransomware: 140 (↑82% since Jan)
Data Breach: 185 (↑31%)
Data Leak: 194 (↑47%)
Web Exploits Tripled
15 (Jan) → 10 (Feb) → 35 (Mar)
Indicates growing targeting of manufacturing websites or applications.
Consistent Growth in Web Hack/Exploit Activity
6 (Jan) → 14 (Feb) → 15 (Mar)
Suggests attackers are increasingly probing for vulnerabilities.
DDoS & Hacktivism Stay Low but Present
DDoS: 11 → 21 → 18
Hacktivism: 3 → 9 → 6
Over the past three months, CYFIRMA’s telemetry has identified 79 mentions of manufacturing out of a total of 4,677 industry mentions. This is from a total of 11,222 CVEs published in 90 days.
The manufacturing industry ranked 11th out of 13 industries in the last 90 days with a share of 1.69% of all detected industry chatter.
Below is a breakdown of 30-day periods of all mentions.
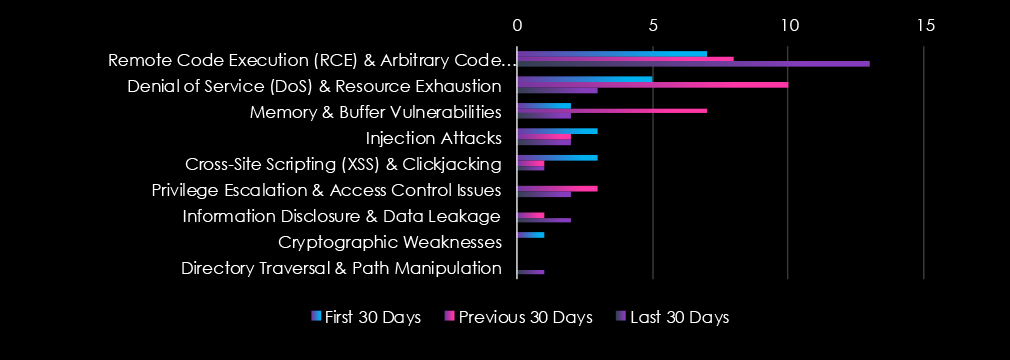
Remote & Arbitrary Code Execution are the most common vulnerabilities along with Denial of Service & Resource Exhaustion and Memory & Buffer vulnerabilities. Later they recorded a notable increase in the middle of the last 90-day period, while the former in the last 30 days.
In total, manufacturing comprises 1.69% of all detected industry vulnerabilities in the last 90 days and ranked as 11th out the 13 industries.
Below are observed key trends across 90 days.
Moderate but Fluctuating Activity
Jan: 21 → Feb: 32 → Mar: 26
Peak in February, followed by a slight drop in March.
Most Common Vulnerabilities (March 2025)
Remote Code Execution (RCE): 13 (↑86% from Jan)
Privilege Escalation: 2 (down from 3 in Feb)
Memory/Buffer Vulnerabilities & Injection Attacks: 2 each
Denial of Service (DoS): Dropped from 10 in Feb to 3 in Mar
RCE Remains a Key Risk
RCE is consistently present and rising again in March, indicating persistent exploit potential.
Low But Persistent Threats Across Categories
Most categories (XSS, Injection, Privilege Escalation, DoS) have low but stable mentions across all three months.
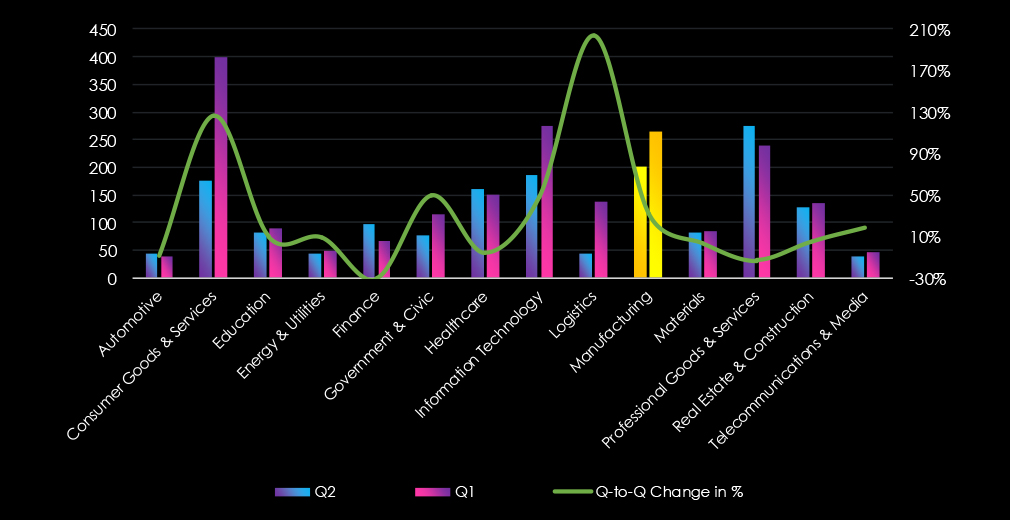
In the past 90 days, CYFIRMA has identified 265 verified ransomware victims in the manufacturing industry. This accounts for 12.5% of the overall total of 2,123 ransomware victims during the same period, placing the manufacturing industry 3rd out of 13 industries.
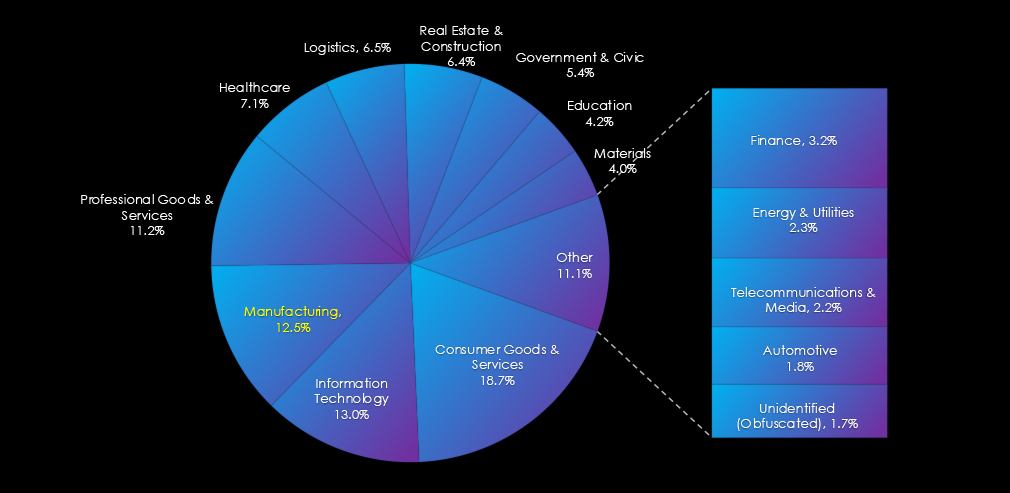
Furthermore, a quarterly comparison reveals an increase of 31% in interest in the manufacturing industry from 201 to 238 victims. The overall share increased from 12.1% to 12.5%.
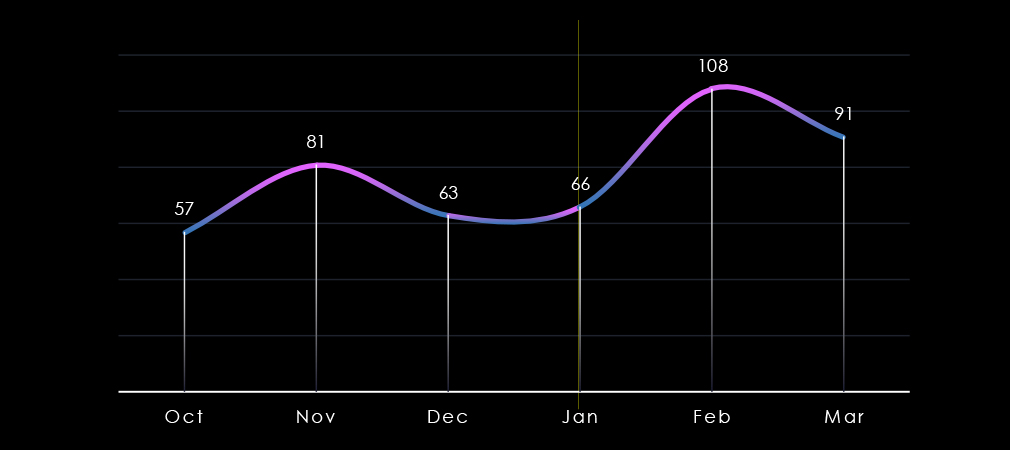
Over the past 180 days, we have observed mildly swinging activity across months with a notable spike during February and only a minor decrease in March.
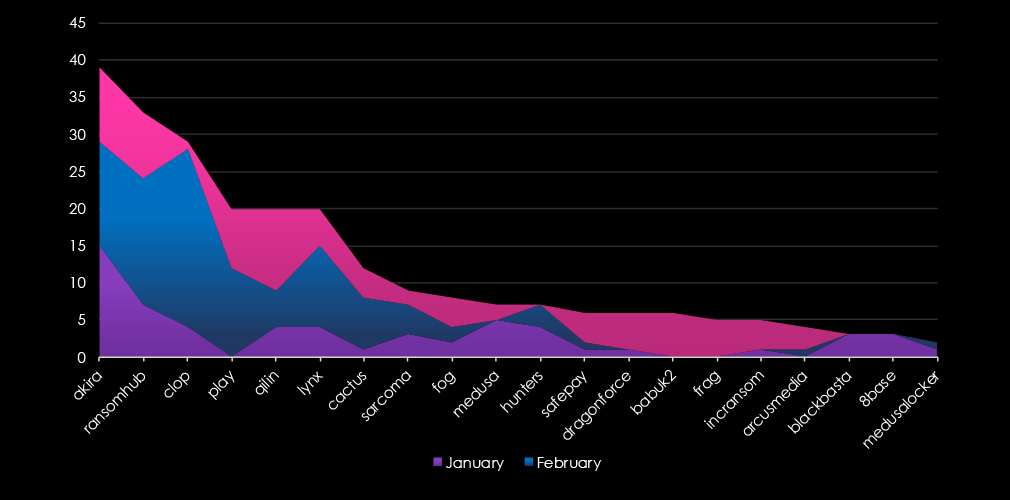
A breakdown of the top 20 gangs’ monthly activity provides insights into which gangs were active each month. For example, the third most active gang Cl0p has recorded nearly all victims in February. On the other hand, Akira and RansomHub were active across all three months.
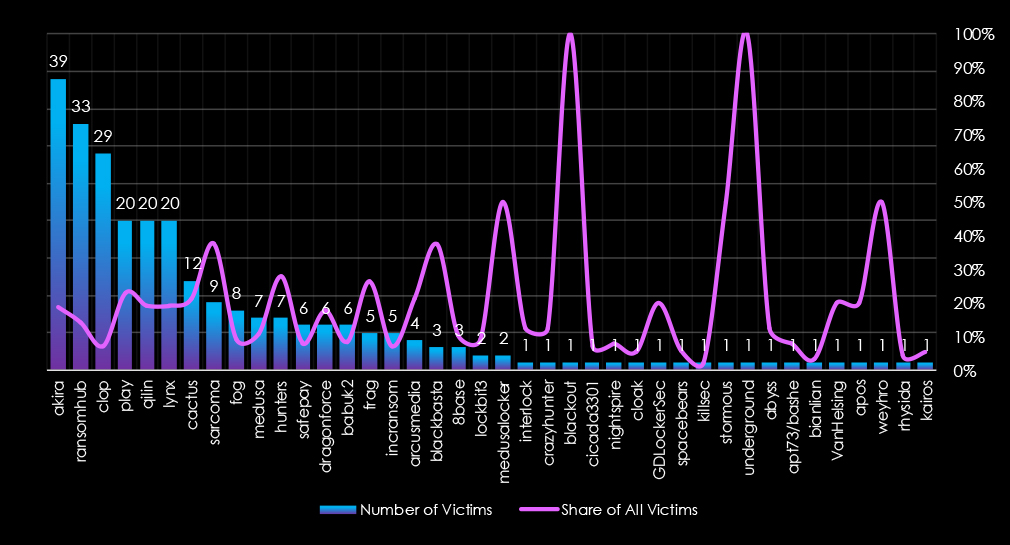
In total 40 out of 69 gangs were active in last 90 days. Akira gang recorded the most victims (39), followed by RansomHub (33) and Cl0p (29).
The share of all victims for most gangs in this industry is relatively high. Out of the top 10 gangs, only two have a share of below 10% of victims in the manufacturing industry.
Akira, Play, Qilin, Lynx, and Cactus recorded around 20% of all their victims in this industry. Sarcoma has the highest share of 37.5% among top gangs.
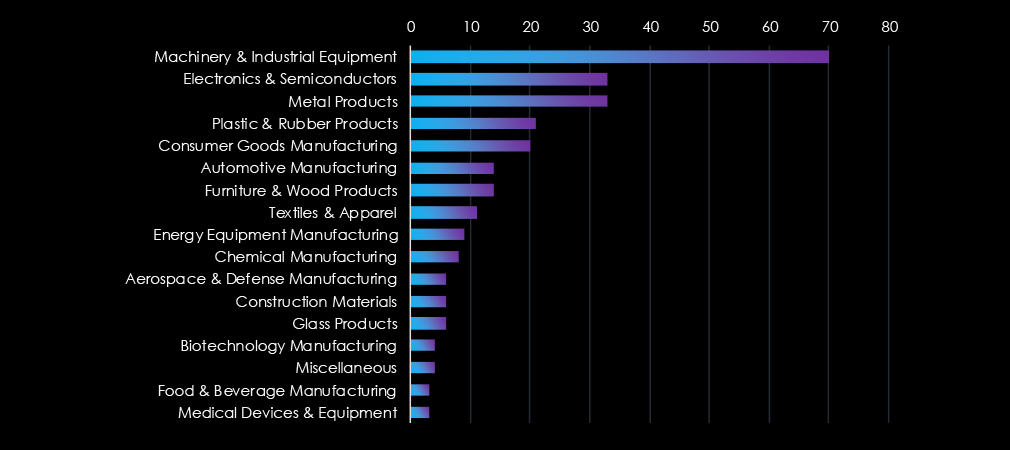
Machinery & Industrial equipment are by far the most frequent victims in the manufacturing industry. Second and third are Electronics & Semiconductors and Metal products.
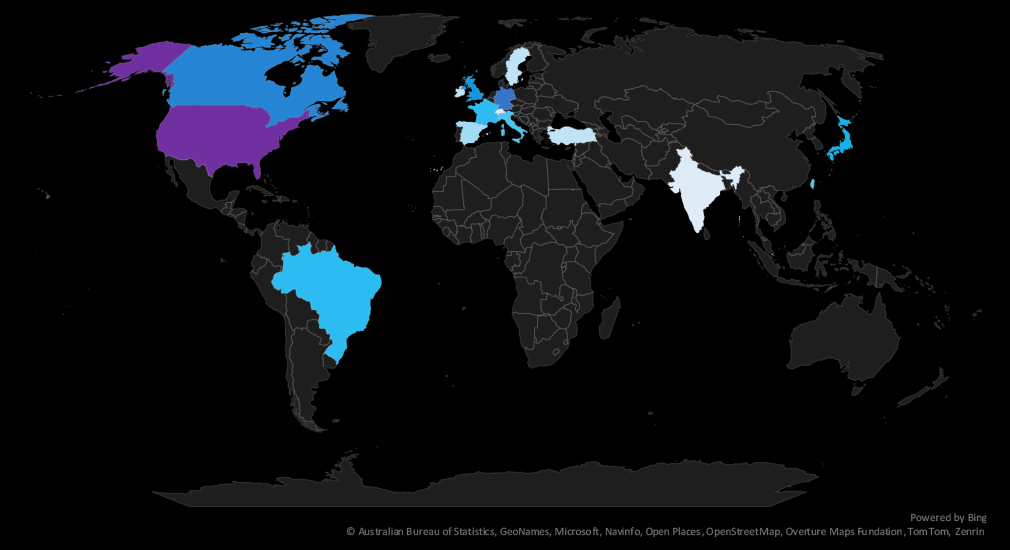
The geographic distribution heatmap underscores the widespread impact of ransomware, highlighting the countries where victims in this industry have been recorded. Notable is growing presence in Latin America.
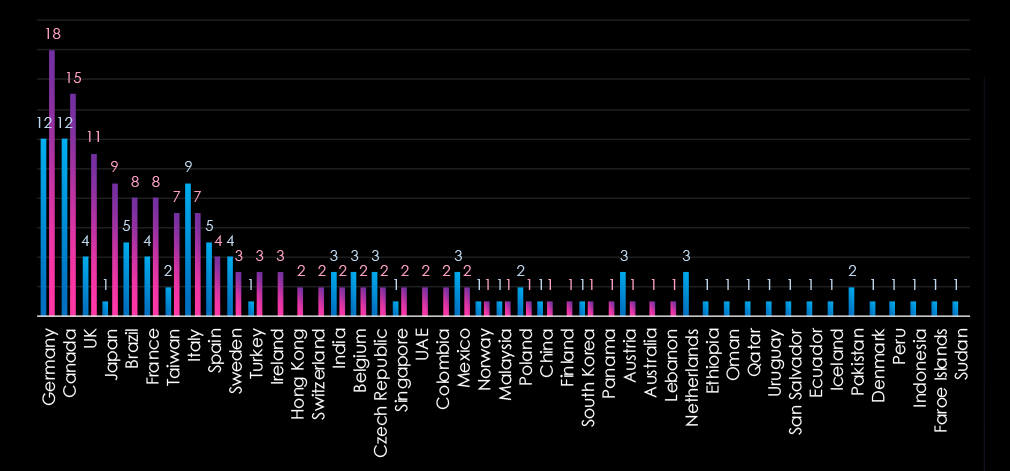
The chart shows quarter-to-quarter changes in targeted countries. Data is sorted by the last 90 days and compared to the previous 90 days marked blue, omitting the USA from the chart to avoid skewing the scale.
The USA recorded 139 victims in the last 90 days representing 52% of all victims.
The manufacturing industry is placed as the third most frequent victim recording 265 victims in the last 90 days.
Overall share increased from 12.1%% to 12.5% of all ransomware victims.
Monthly Activity Trends
After a month of relatively stable numbers, we observed a spike during February caused by the Cl0p ransomware rampage. In March activity slowed down but remained elevated.
Akira was the most active gang overall followed by RansomHub and Cl0p.
Ransomware Gangs
A total of 40 out of 69 active ransomware groups targeted this industry in the past 90 days:
Akira: The most active with 39 victims and 18.8% of their victims from the manufacturing sectors (39 out of 207 victims).
Sarcoma: Highest share of 37.5% victims in this industry (9 out of 24 victims), suggesting focused interest.
Overall 8 out of the top 10 gangs recorded around 20% share of their victims in manufacturing, underlining high risk for the industry.
Geographic Distribution
The geographic distribution of ransomware victims in the manufacturing industry is mostly represented by the USA (139), accounting for 52% of all victims. Germany, Canada, the UK, Japan, and Brazil are in the top 5 most attacked countries.
In total, 31 countries recorded ransomware victims in this industry in last 90 days, which is a decline from 36 countries in the previous 90 days.
For a comprehensive, up-to-date global ransomware tracking report, please refer to our new monthly “Tracking Ransomware” series here.
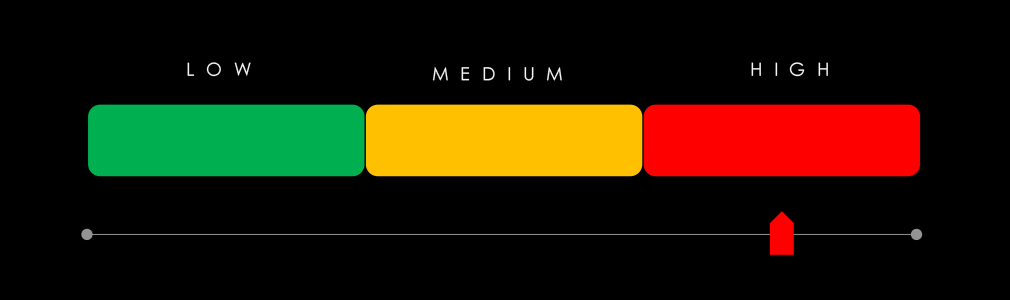
Over the past 90 days, the manufacturing industry faced a high risk from APT campaigns, significant ransomware activity, low dark web chatter, and a relatively low but persistent level of vulnerabilities:
APT Campaigns: All observed campaigns (5 out of 5) targeted manufacturing, a 100% presence—a rise in proportional terms despite one fewer campaign than the previous period. Activity spiked in February and carried into March. Chinese threat actors Salt Typhoon and Volt Typhoon led about half of the incidents, with financially motivated Thai, Vietnamese, and English-speaking groups involved as well. Attacks impacted 20 countries, notably Japan and Thailand, and exploited a broad range of technologies (web apps, OS, routers, network monitoring, etc.).
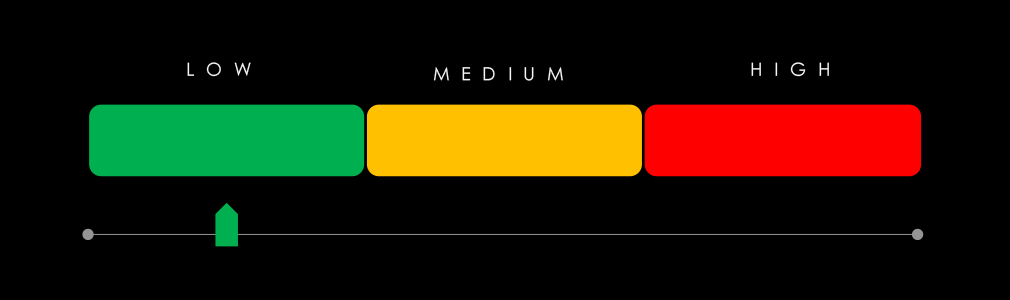
Underground & Dark Web Chatter: Manufacturing accounted for 2.76% of industry chatter, ranking 10th out of 13. Threat mentions jumped 54% from January to March, focusing on ransomware, data breaches, data leaks, and growing web exploits. Although DDoS and hacktivism activity remained relatively low, the surge in web-based attacks suggests more adversaries probing for manufacturing-related vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities: Representing 1.69% of industry-related vulnerabilities, manufacturing ranked 11th. Overall mentions peaked in February before a slight dip in March. Remote code execution (RCE) consistently posed the greatest risk, with an 86% increase in March. Other categories—privilege escalation, injection attacks, denial of service, and XSS—remained low but present.
Ransomware: Manufacturing placed as the third most frequent ransomware target, with 265 victims (12.5% share, up from 12.1%). A spike in February was driven by Clop; activity eased in March but stayed elevated. Of 69 active gangs, 40 targeted manufacturing. Akira had the most confirmed victims (18.8% in manufacturing), while Sarcoma showed the highest proportional focus (37.5%). The U.S. accounted for 52% of identified victims, followed by Germany, Canada, the U.K., Japan, and Brazil, with incidents reported in 31 countries.