Published On : 2025-04-17
Earth Estries is a Chinese Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group that has gained prominence for its sophisticated cyber espionage activities targeting critical infrastructure and government entities globally.
Alias: Famous Sparrow, Ghost Emperor, Salt Typhoon, UNC2286
Target Technologies: VPS, Windows, IoT
Motivation: Espionage, Data Exfiltration
Targeted Regions: Asia, North America, Middle East, Europe and South Africa.
Targeted Industries
Techniques Used: Keylogging, Malware Implant, DLL Sideloading
Targeted Countries:
The United States, Germany, South Africa, Malaysia, the Philippines, Taiwan, India, Canada, and Singapore.

Malware used by Earth Estries: HemiGate, GHOSTSPIDE, Zingdoor, Cobalt Strike, MASOL RAT, SNAPPYBE
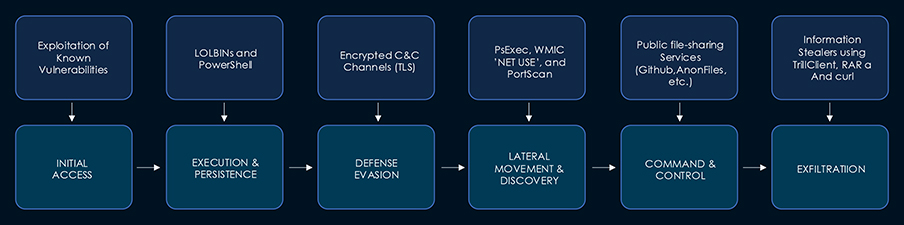
EARTH ESTRIES ATTACK FLOW
Recently Exploited Vulnerabilities by Earth Estries
- CVE-2024-20399
- CVE-2023-20273
- CVE-2023-20198
- CVE-2024-21887
- CVE-2023-46805
Earth Estries’s Recent Campaigns Highlights and Trends
Earth Estries has conducted several notable campaigns targeting a broad range of victims:
- Sustained Telecommunications Targeting: A long-term campaign (“Campaign Beta”) impacting telecom providers across Asia (Taiwan, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, Philippines, Afghanistan, India, Pakistan, Malaysia) and the United States. This involves the use of DEMODEX, GHOSTSPIDER, and SNAPPYBEE malware. Recent reports indicate breaches affecting major US carriers.
- Government & Related Entities Focus: Campaigns (“Campaign Alpha”) targeting government agencies, as well as associated organizations like consulting firms and NGOs (particularly those working with US government/military) in the APAC region, US, South Africa, and Middle East. These campaigns leverage tools like DEMODEX, SNAPPYBEE, and Cobalt Strike.
- Broad Sector Targeting: Compromises have been confirmed across over 20 organizations spanning the Telecommunications, Technology, Government, NGOs, Consulting, Chemical, Transportation, Aviation, and Property sectors.
- Geographic Scope: Victims identified in the US, Taiwan, Philippines, Thailand, South Africa, Vietnam, India, Indonesia, Afghanistan, Brazil, Malaysia, Pakistan, Eswatini, and Germany.
Observed Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs):
- Initial Access: Exploitation of known vulnerabilities in public-facing applications and devices is a primary vector. Key targets include Microsoft Exchange (ProxyLogon CVEs), Ivanti Connect Secure (CVE-2023-46805 CVSS Score: 8.2, CVE-2024-21887 CVSS Score: 9.1), FortiClient EMS (CVE-2023-48788 CVSS Score: 9.8), and Sophos Firewall (CVE-2022-3236 CVSS Score: 9.8).
- Execution & Persistence: Heavy reliance on LOLBINs (PSEXEC, WMIC, curl, regsvr32, etc.) and PowerShell (including downgrade attacks to evade AMSI). They deploy custom backdoors (GHOSTSPIDER, MASOL RAT, Zingdoor, Crowdoor) and rootkits (DEMODEX) for long-term persistence, often using scheduled tasks and registry modifications. DLL Sideloading, sometimes using decade-old legitimate files, is frequently observed.
- Defense Evasion: Techniques include operating primarily in-memory, using encrypted C&C channels (TLS), cleaning up malware artifacts post-operation, using CAB files for payload delivery, and masquerading.
- Lateral Movement & Discovery: Utilization of tools like PsExec, WMIC, ‘net use’, and PortScan to map networks and move laterally.
- Command & Control: Employs complex C&C infrastructure, potentially managed by separate teams. Evidence suggests the use of multi-hop proxies and abuse of public file-sharing services (Github, AnonFiles, etc.) for command/data transfer.
- Exfiltration: Information stealers like TrillClient are used alongside utilities like RAR (for archiving) and curl (for uploading data to file-sharing sites).






